With methods of so-called geoengineering, the climate could theoretically be artificially influenced and cooled. Bernese researchers have now investigated whether it would be possible to prevent the melting of the West Antarctic ice sheet by artificially "darkening the sun". The results show that artificial influence cannot be achieved without decarbonisation and entails high risks.
Read the original press release here.
With methods of so-called geoengineering, the climate could theoretically be artificially influenced and cooled. Bernese researchers have now investigated whether it would be possible to prevent the melting of the West Antarctic ice sheet by artificially "darkening the sun". The results show that artificial influence cannot be achieved without decarbonisation and entails high risks.
Is there an emergency solution that could stop climate change? Technical methods that artificially influence the climate have been discussed for some time under the term geoengineering. However, the majority of climate researchers have been critical of them until now: high risks, incalculable consequences for future generations.
In a publication just published in the journal Nature Climate Change, researchers led by Johannes Sutter from the Climate and Environmental Physics Division (KUP) at the Institute of Physics and the Oeschger Centre for Climate Research at the University of Bern are now investigating the question of whether the melting of the ice in West Antarctica could be prevented by artificially influencing solar radiation. The researchers also warn of unforeseeable side effects of geoengineering.
Avoiding a key climate tipping point
"The window of opportunity to limit the global temperature increase to below 2 degrees is closing fast," says ice modelling specialist Johannes Sutter, "so it is possible that technical measures to influence the climate will be seriously considered in the future." Therefore, he says, it is necessary to investigate the effects and risks of "solar radiation management" in theoretical models. Solar Radiation Management (SRM) is a term used to describe various methods of blocking solar radiation in order to make the Earth cooler.
A key reason for the increased interest in geoengineering is the avoidance of tipping points at which the climate could change abruptly and irreversibly. These include the melting of the West Antarctic and Greenland ice sheets and the associated metre-high rise in sea level. "Observations of the ice flows in West Antarctica indicate that we are very close to a so-called tipping point or have already passed it," explains Johannes Sutter, "so we wanted to find out with our study whether a collapse of the ice sheet could theoretically be prevented with solar radiation management."
Artificially dimming the sun
Specifically, Sutter and his colleagues have investigated what would happen if so-called aerosols - suspended particles in a gas - introduced into the stratosphere succeeded in blocking solar radiation from the Earth - darkening the sun, so to speak. So far, research has mainly focused on the global effects of Solar Radiation Management (SRM). The Bern study is the first to use ice model simulations to show what effect such a measure would have on the Antarctic ice sheet. The study examines the possible development of the ice sheet under different future greenhouse gas scenarios and comes to differentiated results: If emissions continue unabated and the SRM takes place in the middle of this century, the collapse of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet could be delayed somewhat, but not prevented. In a medium emissions scenario, SRM applied until the middle of the century could prove to be an "effective tool" to slow down or even prevent the ice sheet collapse.
According to the model calculations, SRM works best when it occurs as early as possible and is combined with ambitious climate protection measures. However, as the study authors point out, "our simulations show that the most effective way to prevent long-term collapse of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet is rapid decarbonisation". The chances of a stable ice sheet in the longer term are greatest if greenhouse gas emissions were reduced to net zero "without delay".
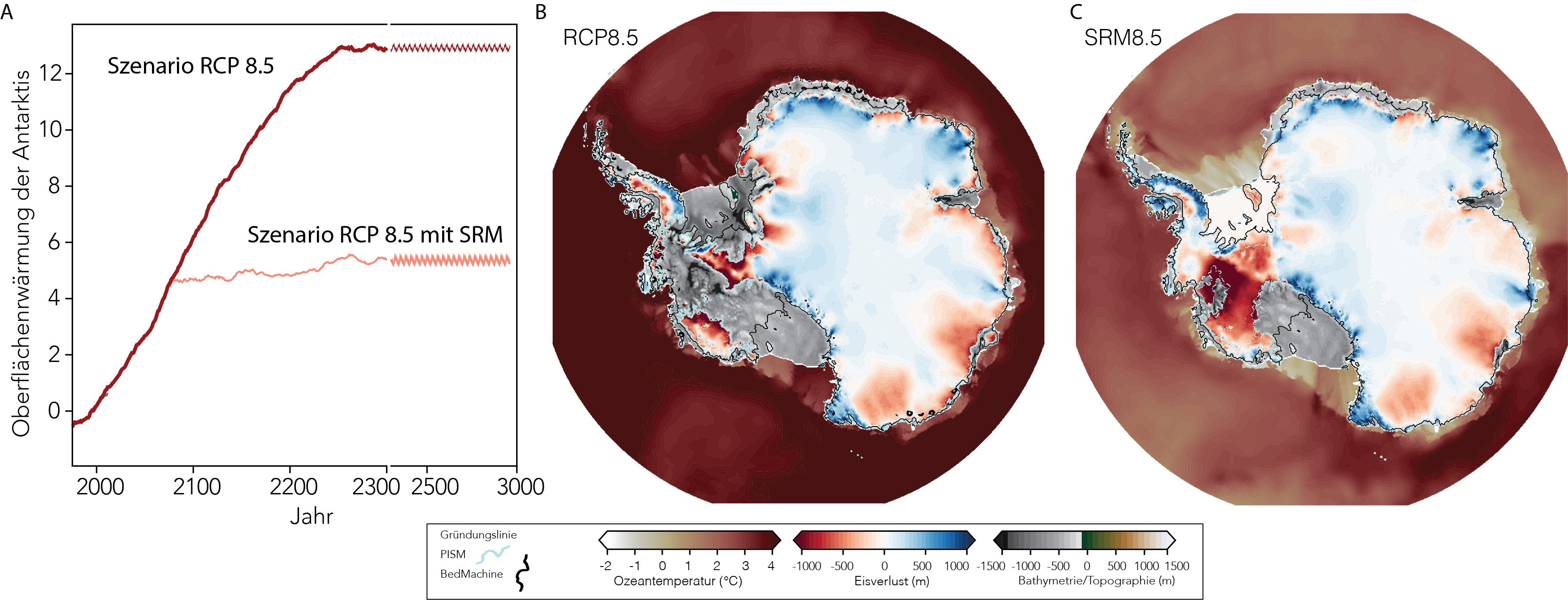
Image: Courtesy of study authors
Possible side effects still hardly studied
But how should one imagine a dimming of the sun in practical terms? According to Johannes Sutter, a whole fleet of extremely high-flying aircraft would have to spread millions of tonnes of aerosols in the stratosphere. However, this technical intervention in the climate would have to be maintained without interruption and for centuries. If the intervention were stopped as long as the greenhouse concentration in the atmosphere remained high, the temperature on Earth would rise by several degrees.
The consequences of such a termination shock, Johannes Sutter points out, are only one of the possible dangers posed by SRM. The potential side effects are still insufficiently researched, but they range from a shift in the monsoon regime to changes in ocean and atmospheric circulation. Ocean acidification would also continue to advance. Critical voices also warn of political and social effects: The use of techniques such as dimming the sun could lead to climate protection measures being slowed down or even prevented. Thomas Stocker, professor of climate and environmental physics at the University of Bern and co-author of the study, says: "Geoengineering would be another global experiment and a potentially dangerous human intervention in the climate system, which according to Article 2 of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change should be prevented at all costs."
Oeschger Center for Climate Research
The Oeschger Center for Climate Change Research (OCCR) is one of the strategic centers of the University of Bern. It brings together researchers from 14 institutes and four faculties. The OCCR conducts interdisciplinary research at the cutting edge of climate change research. The Oeschger Center was founded in 2007 and bears the name of Hans Oeschger (1927-1998), a pioneer of modern climate research, who worked in Bern.
Further information: www.oeschger.unibe.ch